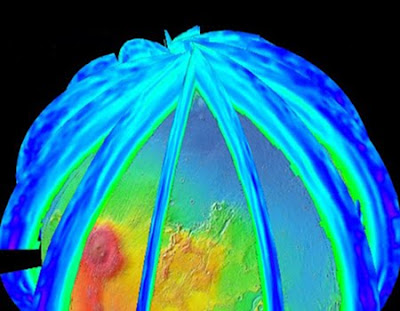
One of the instruments on a 2016 mission to orbit Mars will provide daily maps of global, pole-to-pole, vertical distributions of the temperature, dust, water vapor and ice clouds in the Martian atmosphere. The joint European-American mission, ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter, will seek faint gaseous clues about possible life on Mars. This instrument, called the ExoMars Climate Sounder, will supply crucial context with its daily profiling of the atmosphere's changing structure. The European Space Agency and NASA have selected five instruments for ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter. The European Space Agency will provide one instrument and the spacecraft. NASA will provide four instruments, including ExoMars Climate Sounder, which is coming from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
Two of the other selected instruments are spectrometers one each from Europe and the United States designed to detect very low concentrations of methane and other important trace gases in the Martian atmosphere. "To put the trace-gas measurements into context, you need to know the background structure and circulation of the atmosphere," said JPL's Tim Schofield, principal investigator for the ExoMars Climate Sounder. "We will provide the information needed to understand the distribution of trace gases identified by the spectrometers. We'll do this by characterizing the role of atmospheric circulation and aerosols, such as dust and ice, in trace-gas transport and in chemical reactions in the atmosphere affecting trace gases."
The ExoMars Climate Sounder is an infrared radiometer designed to operate continuously, day and night, from the spacecraft's orbit about 400 kilometers (about 250 miles) above the Martian surface. It can pivot to point downward or toward the horizon, measuring temperature, water vapor, dust and ices for each 5-kilometer (3-mile) increment in height throughout the atmosphere from ground level to 90 kilometers (56 miles) altitude. Schofield and his international team have two other main goals for the investigation, besides aiding in interpretation of trace-gas detections. One is to extend the climate mapping record currently coming from a similar instrument, the Mars Climate Sounder, on NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, which has been working at Mars since 2006.
Two of the other selected instruments are spectrometers one each from Europe and the United States designed to detect very low concentrations of methane and other important trace gases in the Martian atmosphere. "To put the trace-gas measurements into context, you need to know the background structure and circulation of the atmosphere," said JPL's Tim Schofield, principal investigator for the ExoMars Climate Sounder. "We will provide the information needed to understand the distribution of trace gases identified by the spectrometers. We'll do this by characterizing the role of atmospheric circulation and aerosols, such as dust and ice, in trace-gas transport and in chemical reactions in the atmosphere affecting trace gases."
The ExoMars Climate Sounder is an infrared radiometer designed to operate continuously, day and night, from the spacecraft's orbit about 400 kilometers (about 250 miles) above the Martian surface. It can pivot to point downward or toward the horizon, measuring temperature, water vapor, dust and ices for each 5-kilometer (3-mile) increment in height throughout the atmosphere from ground level to 90 kilometers (56 miles) altitude. Schofield and his international team have two other main goals for the investigation, besides aiding in interpretation of trace-gas detections. One is to extend the climate mapping record currently coming from a similar instrument, the Mars Climate Sounder, on NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, which has been working at Mars since 2006.
View this site : Property auctions
No comments:
Post a Comment